Fill Out a Valid Tennessee Fae 173 Form
Understanding the nuances of tax procedures can often seem overwhelming, yet the Tennessee FAE 173 form serves as a critical tool for businesses navigating the complexities of franchise and excise tax requirements in the state. Designed by the Tennessee Department of Revenue, this form specifically facilitates the application process for an extension of time to file the franchise and excise tax returns. Recognizing the necessity of meeting taxpayers' needs for additional time under certain circumstances, the form clearly outlines a six-month grace period from the original filing deadline, provided that applicants adhere to the detailed prerequisites set forth. Not only does the form require the taxpayer's basic identification and contact information, but it also mandates a meticulous financial declaration, anticipated to be settled through the attachment of a calculated worksheet. This worksheet critically evaluates estimated taxes due, incorporating any potential adjustments from prior payments or credits. Furthermore, the form delineates the conditions for submission, including distinct stipulations regarding the coordination of payments corresponding with the original versus the extended due dates, and emphasizes the importance of satisfactory payment to preempt penalties. The reverse side of the form extends additional guidance, effectively demystifying the operational expectations and ensuring compliance through a step-by-step breakdown. As a medium for request submission, the FAE 173 underscores the Tennessee Department of Revenue's commitment to providing procedural clarity and support to taxpayers aiming to navigate their fiscal responsibilities successfully.
Example - Tennessee Fae 173 Form
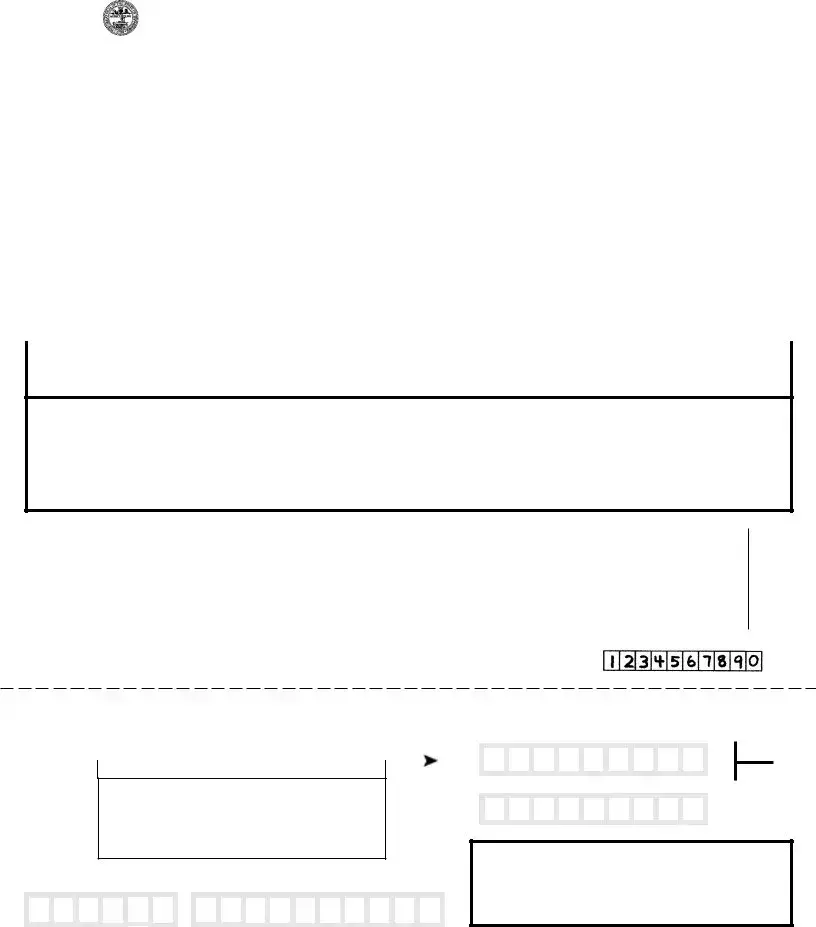
TENNESSEE DEPARTMENT OF REVENUE
APPLICATION FOR EXTENSION OF TIME TO FILE
FRANCHISE, EXCISE TAX RETURN
|
FAE |
Taxable Year |
|
Account No. |
FEINorSSN |
|
|
Beginning: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
173 |
Ending: |
|
Due Date |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Make your check payable to the Tennessee |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Department of Revenue for the amount shown on |
|
|
TAXPAYER NAME AND MAILING ADDRESS |
|
|
Line 4 of the worksheet and mail to: |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
NAME ___________________________________________________________________ |
|
Tennessee Department of Revenue |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BOX(STREET) ____________________________________________________________ |
|
Andrew Jackson State Office Bldg. |
|||
|
|
500 Deaderick Street |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CITY ____________________________________________________________________ |
|
Nashville, TN 37242 |
|||
|
|
|
||||
|
STATE ________________ ZIP __________________________ |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
An extension of time of six (6) months will be granted, provided you meet the requirements outlined on the reverse side of the form.
REMINDERS
1)Enter account number or FEIN in the spaces provided.
2)Quarterly estimated tax payments made for the year, available tax credits, and overpayments from prior years should be deducted when computing the payment due.
3)If previous year's credit(s) and current year's estimated tax payment exceed estimated liability, enter 0 on Line 4.
4)Sign and date your return in the signature box below.
5)See reverse side for additional procedures for obtaining an extension of time.
WORKSHEETFORCOMPUTATIONOFEXTENSIONPAYMENT
1.EstimatedFranchiseTaxcurrentyear .....................................................................................................................
2.EstimatedExciseTaxcurrentyear ............................................................................................................................
3.Deduct: Prior year's overpayment, estimated payments and tax credits for current year ..........................................
4.Amount due with extension request (Lines 1 and 2 less Line 3; if Line 3 is greater than total
of Lines 1 and 2, enter 0 and return form without payment) ......................................................................................
Keep Upper Portion For Your Records
 Return Copy Below - Detach Here
Return Copy Below - Detach Here 
ROUND TO NEAREST DOLLAR
00
___________________________00
00
00
WRITENUMBERSLIKETHIS
FAE
173
TENNESSEE DEPARTMENT OF REVENUE
Application for Extension of Time to File Franchise, Excise Tax
Filing |
|
Extended |
|
Period |
|
DueDate |
|
|
|
|
|
ACCOUNT
FOROFFICEUSEONLY
If your account number is not preprinted or unknown, enter federal identification number/social security number.
(FEIN/
SSN)
AMOUNT DUE
(Line 4 of  00 worksheet)
00 worksheet)
Under penalties of perjury, I declare that I have examined this report, and to the best of my knowledge and belief, it is true, correct, and complete.
________________________________________ |
_________ |
______________ |
|||
Taxpayer's Signature |
|
Date |
|
|
Title |
________________________________________ |
_________ |
______________ |
|||
Tax Preparer's Signature |
|
Date |
|
Telephone |
|
________________________________ |
____________ |
_________ |
_______ |
||
Preparer's Address |
City |
|
|
State |
ZIP |
INTERNET |

PROCEDURES FOR OBTAINING AN EXTENSION OF TIME
NOTE: This form can be filed electronically free of charge at apps.tn.gov/fnetax
1.Required Payment:
•Payments equal to the lesser of 100% of the prior year tax liability or 90% of the current year tax liability must be made by the original due date.
•If the prior tax year covered less than twelve months, the prior period tax must be annualized when calculating the required payment.
•If there was no liability for the prior year, the required payment is $100.
•Quarterly estimated payments, prior year overpayments and any other
2.Extension requests should be made as follows:
•If you are not required to make a payment because you have already made sufficient payments, either the state form or a copy of your federal extension request can be submitted. The form or copy of the federal extension need not be filed on the original due date of the return. Instead, it should be attached to the return itself, which is to be filed on or before the extended due date.
•If a payment is needed to meet the payment requirement and you do not file your federal return as part of a consolidated group, either the state form or a copy of your federal extension request can be submitted. In this case, the form or copy of your federal extension must be filed with the extension payment on or before the original due date of the return.
•If a payment is required and you file your federal return as part of a consolidated group, you must use this form or file an extension request electronically. This form or the electronic version of this form must be filed with the extension payment on or before the original due date of the return.
3.Other important information:
•Penalty will be computed as though no extension had been granted if, (1) the amount paid on or before the original due date does not satisfy the payment requirement indicated above, or (2) the return is not filed by the extended due date.
•An approved extension does not affect interest. Interest will be computed on any unpaid tax from the original due date of the return until the date the tax is paid.
Form Breakdown
| Fact Name | Detail |
|---|---|
| Form Designation | FAE 173 |
| Purpose | Application for Extension of Time to File Franchise, Excise Tax Return |
| Governing Body | Tennessee Department of Revenue |
| Extension Period Granted | Six (6) months |
| Required Payment Calculation | Lesser of 100% of prior year tax liability or 90% of current year tax liability |
| Alternative for No Prior Year Liability | Required payment is $100 if there was no liability for the prior year |
| Penalty Conditions | Penalty applicable if the payment made by the original due date doesn't meet the required payment, or if the return isn't filed by the extended due date |
| Interest on Unpaid Tax | Interest computed from the original due date of the return until the tax is paid |
Detailed Instructions for Filling Out Tennessee Fae 173
When it comes to navigating the intricacies of tax payments and deadlines, the Tennessee Department of Revenue tries to offer some flexibility by allowing an extension for filing the Franchise and Excise tax returns. This extension, formally requested through the FAE 173 form, grants taxpayers an additional six months to file their return. Understanding and accurately filling out this form is vital for those who are aiming to avoid penalties and ensure that their tax processes run smoothly. Here are step-by-step instructions to guide you through completing the form correctly.
- Start by entering the taxpayer name and mailing address in the designated section. This should include the name, box or street address, city, state, and zip code.
- Indicate the taxable year's beginning and ending dates, alongside the due date and your account number or Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN) / Social Security Number (SSN) in the spaces provided at the top of the form.
- In the worksheet for computation of extension payment section, calculate your estimated franchise and excise tax for the current year and enter these amounts in Lines 1 and 2, respectively.
- Subtract any prior year's overpayment, estimated payments, and tax credits for the current year from the total of estimated taxes (the result goes in Line 3).
- Determine the amount due with your extension request by subtracting Line 3 from the total of Lines 1 and 2. If Line 3 is greater than the total, enter 0 on Line 4. This means you won't need to send a payment with the form.
- Write the amount from Line 4 of the worksheet in the "AMOUNT DUE" section near the bottom of the form.
- Sign and date the form in the provided signature section at the bottom. If a tax preparer completed this form, ensure they sign and date it as well, including their telephone number and address.
- If a payment is required, make a check payable to the Tennessee Department of Revenue for the amount shown on Line 4. Mail this check along with your completed form to the Tennessee Department of Revenue at the Andrew Jackson State Office Building, 500 Deaderick Street, Nashville, TN 37242.
After taking these steps, note that if your calculated payment does not meet the required threshold based on either last year's tax or the current year's estimated tax, penalties might apply. Also, remember that interest will accrue on any unpaid tax from the original due date, regardless of the granted extension. Always double-check your work and consult with a tax professional if you are unsure. This careful attention to detail and adherence to the submission guidelines will ensure a smoother process in managing your tax responsibilities.
More About Tennessee Fae 173
What is the Tennessee FAE 173 form?
The Tennessee FAE 173 form is an application for an extension of time to file franchise and excise tax returns with the Tennessee Department of Revenue. It allows taxpayers to request an additional six months to file their taxes beyond the original due date, subject to certain conditions outlined on the form.
Who needs to file the Tennessee FAE 173 form?
Any taxpayer who is subject to franchise and excise taxes in Tennessee and cannot file their return by the original due date may need to file the FAE 173 form to request an extension.
How do I determine the amount due with my extension request?
To determine the amount due with your extension request, complete the worksheet provided on the form. Calculate your estimated franchise and excise taxes for the current year, deduct any overpayments, estimated payments, and tax credits from the previous year, and enter the net amount due on Line 4. If your credits and payments exceed your estimated liability, enter 0 and return the form without payment.
Can the FAE 173 form be filed electronically?
Yes, the FAE 173 form can be filed electronically free of charge at the specified Tennessee Department of Revenue website.
What are the payment requirements for the extension to be granted?
- Payments must be equal to the lesser of 100% of the prior year tax liability or 90% of the current year tax liability and made by the original due date.
- If the prior taxed year was less than twelve months, the liability must be annualized to calculate the required payment.
- If there was no liability for the prior year, the minimum required payment is $100.
What happens if I do not meet the payment requirement?
If the amount paid by the original due date does not meet the required payment threshold, a penalty will be computed as if no extension had been granted. Additionally, if the return is not filed by the extended due date, penalties may apply.
Does obtaining an extension affect interest on unpaid taxes?
No, obtaining an extension does not affect the calculation of interest. Interest will be charged on any unpaid tax from the original due date of the return until the tax is paid.
Where should the FAE 173 form and any payment be sent?
The completed form and any payment due should be made payable to the Tennessee Department of Revenue and mailed to their office, located at the Andrew Jackson State Office Bldg., 500 Deaderick Street, Nashville, TN 37242.
What information is required on the FAE 173 form?
- Taxpayer name and mailing address
- Account number or Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN) or Social Security Number (SSN)
- Estimated franchise and excise tax for the current year
- Calculations of payments due with the extension request
- Signature of the taxpayer and date
Is it possible to use a copy of my federal extension request when submitting the FAE 173 form?
Yes, if you are not part of a consolidated group and have already made sufficient payments to meet the extension payment requirement, a copy of your federal extension request can be submitted instead of or along with the state form.
Common mistakes
Filling out the Tennessee FAE 173 form, which is an application for an extension of time to file the Franchise and Excise Tax Return, can seem straightforward. However, there are common oversights that individuals make during this process. These mistakes can lead to delays, incorrect filings, and sometimes penalties. Knowing what these errors are can help ensure that the process goes smoothly and the application is processed efficiently.
One of the first mistakes is not entering the account number or Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN) in the designated spaces. This information is critical for identifying the taxpayer's account and ensuring that the extension is applied correctly. Another error is in the calculation of the estimated taxes and payments. Frequently, taxpayers do not accurately deduct quarterly estimated tax payments, available tax credits, and overpayments from prior years, leading to incorrect amounts being reported on Line 4 of the worksheet.
Additionally, mishandling the amount due with the extension request is a common error. If prior year's credits and the current year's estimated tax payment exceed the estimated liability, "0" should be entered, and the form should be returned without payment. However, taxpayers often miss this step. There's also the issue of failing to sign and date the return. The signature verifies that the information provided is accurate and true to the best of the taxpayer's knowledge, making it a critical final step in the application process.
Here are nine mistakes often made on the Tennessee FAE 173 form:
- Not entering the account number or the FEIN/SSN.
- Miscalculating estimated franchise and excise taxes for the current year.
- Failing to accurately deduct prior year's overpayments, estimated payments, and tax credits for the current year.
- Incorrectly calculating the amount due with the extension request.
- Omitting the taxpayer’s signature and date, which verifies the form’s accuracy.
- Incorrectly rounding numbers to the nearest dollar.
- Mismanagement of required payments, especially in not meeting the lesser of 100% of the prior year's tax liability or 90% of the current year's tax liability by the original due date.
- Not submitting the form or a copy of the federal extension request when no payment is required because of sufficient prior payments.
- Failing to attach the state form or a copy of the federal extension request to the return if submitted after the original due date of the return.
To avoid these common mistakes:
- Double-check the account number or FEIN/SSN entered.
- Review the calculations for estimated taxes to ensure accuracy.
- Verify that all prior payments and tax credits have been correctly deducted.
- Ensure that the form is correctly signed and dated before submission.
- Follow all guidelines for rounding numbers as outlined in the instructions.
- Meet the required payment thresholds to avoid penalties.
- File the state form or a copy of the federal extension request as specified to cater to different payment scenarios.
By avoiding these common errors, taxpayers can ensure a smoother process in filing their Tennessee FAE 173 form. This not only aids in meeting compliance requirements but also minimizes the risk of delays or penalties associated with the franchise and excise tax returns.
Documents used along the form
When preparing to file the Tennessee Department of Revenue Application for Extension of Time to File Franchise, Excise Tax Return (FAE 173), it's crucial to have all necessary documentation ready to ensure a comprehensive and timely submission. Besides the primary form, several other documents and forms may significantly support your filing process.
- Franchise and Excise Tax Return (FAE 174): This is the main return form for reporting franchise and excise taxes in Tennessee, which the extension application (FAE 173) pertains to. It details your taxable activity throughout the year.
- Quarterly Estimated Tax Payment Vouchers (FAE 172): These vouchers are used throughout the fiscal year to make quarterly estimated tax payments. Evidence of these payments is necessary when calculating the amount due with the extension request.
- Annualized Income Installment Method Form (FAE 221): For taxpayers who earn their income unevenly throughout the year, this form helps calculate estimated taxes in a way that matches their income flow, which can affect the extension payment.
- Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File Individual Income Tax Return (IRS Form 4868): If you’re also seeking a federal extension, this form is required by the IRS. A copy may need to be attached to your Tennessee extension application if your payment status necessitates it.
- Tennessee Department of Revenue Change of Address Form: Before filing an extension request, ensure your address is current with the Tennessee Department of Revenue to avoid miscommunication. This form updates your address on record.
- Taxpayer Representation Authorization (RV-F1904201): If you're using a tax preparer or another representative to handle your tax matters, this form grants them the authority to communicate with the Tennessee Department of Revenue on your behalf.
Collecting and preparing these documents alongside the Tennessee FAE 173 form can streamline the extension filing process, ensuring all the necessary information and payments are accurately reported and processed on time. It’s advisable to check with a tax professional to ensure that all the appropriate forms are completed and submitted correctly.
Similar forms
The Federal Form 4868, "Application for Automatic Extension of Time To File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return," shares notable similarities with the Tennessee FAE 173 form. Both forms are designed to provide taxpayers with an extension of time to file their respective tax returns. The federal form applies to personal income taxes, while the Tennessee form is specific to the state's franchise and excise taxes. Both require the taxpayer to estimate their tax liability and ensure any due payment accompanies the request for an extension, underscoring the importance of financial planning and compliance within established deadlines.
The IRS Form 7004, "Application for Automatic Extension of Time To File Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns," is akin to the Tennessee FAE 173 form, as both serve business entities looking to secure more time for filing their detailed tax documents. Whereas Form 7004 addresses federal tax obligations across various business structures, such as corporations and partnerships, the FAE 173 form is specific to Tennessee's franchise and excise tax requirements. Key similarities include the necessity for accurate tax estimations and the provision for an extension, which does not absolve the taxpayer from late payment penalties should the estimated amount fall short of the actual tax liability.
State-specific forms comparable to the Tennessee FAE 173, such as the California Form 3539, "Payment for Automatic Extension for Corporations and Exempt Organizations," also aim to facilitate taxpayers in managing their filing extensions. While the forms cater to different state tax regulations—California's form for corporations and exempt organizations and Tennessee's for franchise and excise taxes—they both mandate the taxpayer to estimate tax liability and ensure payment accompanies the extension request. This process underscores the uniformity in how states manage tax extensions, emphasizing estimated payments to avoid penalties or interest on due taxes.
The Schedule K-1 (Form 1065), used by partnerships to report the share of income, deductions, and credits to partners, has procedural parallels to the Tennessee FAE 173 form in its focus on accurate reporting and timely compliance. Though the K-1 primarily deals with the allocation of income and its tax implications for partners rather than tax extensions, the emphasis on detailed financial information underlines a common theme between these documents: the critical role of precise financial accountability in tax matters. Both documents highlight the importance of ensuring that financial activities are accurately accounted for and reported by the deadlines.
The IRS Form 1120, the U.S. Corporation Income Tax Return, while primarily a tax filing document, shares the underlying principle of timely and accurate financial disclosure found in the Tennessee FAE 173 form. Businesses are required to meticulously report income, gains, losses, deductions, and credits to the federal government through Form 1120, a process involving detailed financial scrutiny similar to what is required for the FAE 173's estimation of franchise and excise tax liabilities. The premium placed on precision and adherence to deadlines in both forms exemplifies the broader responsibility businesses bear in financial reporting and tax compliance.
The U.S. Form 1041, "U.S. Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts," and the Tennessee FAE 173 form share an emphasis on fiduciary duty in financial matters, particularly in the context of tax obligations. Form 1041 requires estates and trusts to report income, deductions, and either distribute or allocate net income to beneficiaries, demonstrating the principle of stewardship in managing and reporting financial resources. Likewise, the FAE 173 form expects Tennessee businesses to duly manage and report their franchise and excise tax responsibilities, underscoring the commitment required in handling financial obligations to the state.
The Form 941, "Employer's Quarterly Federal Tax Return," is another example of a tax-related document emphasizing timely and accurate reporting, similar to the Tennessee FAE 173 form. Form 941 is used by employers to report payroll taxes withheld from employees' wages, along with the employer's portion of Social Security or Medicare tax. Both the Form 941 and FAE 173 encapsulate the principle of regular, detailed financial reporting as a cornerstone of tax compliance. They emphasize the importance of maintaining up-to-date financial records and making necessary payments to tax authorities in a timely manner, illustrating a shared goal of financial responsibility among taxpayers.
The similarity between the Tennessee FAE 173 form and other tax documents, like the ones mentioned, lies in their collective aim to ensure compliance, accuracy, and timeliness in financial and tax reporting. Each form, while serving different tax obligations—be it at the federal level, another state, or a specific tax type—underscores the significance of diligent financial management and the universal practice of adhering to tax regulations and deadlines.
Dos and Don'ts
Filing the Tennessee FAE 173 form requires attention to detail and adherence to specific guidelines to ensure compliance with the state's tax laws. The following lists outline the dos and don'ts when preparing to submit this form for an extension of time to file the franchise and excise tax return.
Things You Should Do
- Ensure that all necessary information, such as the account number or Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN), is accurately entered in the spaces provided.
- Accurately calculate and record the estimated franchise and excise tax for the current year.
- Deduct any quarterly estimated tax payments made during the year, available tax credits, and overpayments from previous years when computing the payment due with the extension request.
- If estimated liabilities are covered by previous year's credits and current year's estimated tax payments, enter '0' on Line 4 of the worksheet and return the form without payment.
- Sign and date the return in the specified signature box to validate the information provided under the penalties of perjury.
- Make checks payable to the Tennessee Department of Revenue for the amount indicated on Line 4 of the worksheet, if payment is due.
- Consider filing the form electronically through the state's official platform for a more efficient process.
- Attach the state form or a copy of your federal extension request to your return if no payment is required due to sufficient prior payments.
Things You Shouldn't Do
- Do not leave the account number or FEIN/SSN fields blank if the information is known or applicable to your tax profile.
- Do not underestimate the amount due by failing to accurately deduct eligible credits and payments, which could lead to owing interest or penalties.
- Do not submit the form without ensuring all calculations are correct and all necessary documentation, such as prior payment records or tax credits, is accounted for.
- Do not ignore the guidelines for extension requests based on your specific filing situation, including whether you’re submitting with a consolidated group or individually.
- Do not overlook the need for a signature, which certifies the truth and accuracy of the information under penalty of perjury.
- Do not delay filing beyond the original or extended due date to avoid penalties and interest on unpaid taxes.
- Do not forget to round numbers to the nearest dollar on the worksheet to ensure accuracy and compliance with form instructions.
- Do not disregard the electronic filing option, which can simplify the submission process and expedite acknowledgment from the Tennessee Department of Revenue.
Misconceptions
Understanding the intricacies of tax documentation is crucial for compliance, yet misconceptions often pervade among taxpayers, particularly regarding specific forms like the Tennessee FAE 173 form. It's essential to debunk these misunderstandings to ensure accurate and timely submissions. Here are six common misconceptions about the Tennessee FAE 173 form and the truths behind them:
- Misconception 1: The FAE 173 Form Grants an Automatic Six-Month Extension to Pay Taxes
This is not accurate. While the FAE 173 form does indeed grant a six-month extension, it is important to note that this extension applies solely to the filing of the Franchise and Excise Tax Return, not to the payment of taxes. Taxpayers are required to estimate and pay their taxes by the original due date to avoid penalties and interest.
- Misconception 2: No Payment is Required with the Extension Request
Many believe that if they file an extension request using the FAE 173 form, they do not need to make any payment until the extended filing date. Contrary to this belief, the form stipulates that a payment—equal to the lesser of 100% of the previous year's tax liability or 90% of the current year's estimated liability—must accompany the extension request unless prior payments cover the estimated liability.
- Misconception 3: The FAE 173 Form is Only for Businesses Filing as a Consolidated Group
This misconception likely arises from misunderstanding the form's instructions. While specific guidelines are indeed outlined for businesses filing as part of a consolidated group, the FAE 173 form is applicable to all businesses subject to franchise and excise taxes in Tennessee, not just those filing consolidated returns.
- Misconception 4: Overpayments and Credits Do Not Affect the Extension Payment
Another common error is overlooking the impact of overpayments and credits on the extension payment calculation. In reality, these amounts should be deducted when computing the payment due with the extension request, potentially reducing the amount owed or even eliminating the need for an extension payment altogether.
- Misconception 5: Filing the FAE 173 Form Extends the Time to Pay Interest and Penalties
Many mistakenly believe that obtaining an extension to file also extends the period for incurring interest and penalties on unpaid taxes. However, interest will accrue on any unpaid tax from the original due date, regardless of the granted extension for filing. If the required payment is not made by the original due date, penalties may also be assessed.
- Misconception 6: The FAE 173 Form Must be Filed by Mail
With the increasing convenience of digital submissions across various platforms, the assumption that the FAE 173 must be filed exclusively by mail is outdated. Taxpayers have the option to file this form electronically through the state's official website, offering a more efficient and immediate submission process.
Clearing up these misconceptions is vital for taxpayers subject to Tennessee's Franchise and Excise taxes. Ensuring accurate and timely compliance with the state's tax requirements helps avoid unnecessary penalties and interest, contributing to a more straightforward and stress-free tax filing experience.
Key takeaways
When completing and using the Tennessee FAE 173 form, several key points need to be considered for a smooth experience:
- Accurate information is crucial: Ensure the taxpayer's name, mailing address, account number or FEIN/SSN, and all other required fields are correctly filled out to prevent processing delays.
- Understanding payment requirements: Payments must be equal to the lesser of 100% of the prior year's tax liability or 90% of the current year's tax liability to be made by the due date. This guarantees that an extension of six months will be granted. If there was no liability in the prior year, the required payment is $100.
- Filing options: Taxpayers can submit their extension request in multiple ways. If no payment is necessary due to sufficient pre-payments, submission of the Tennessee form or a copy of the federal extension request at any time before the extended due date is acceptable. Otherwise, the form or federal extension copy, along with any necessary payment, must be submitted by the original return due date. Consolidated filers must use this form or file electronically.
- Penalties and interest: If the extension payment does not meet the required amount by the original due date or if the return is not filed by the extended due date, penalties will be imposed as though no extension had been granted. Additionally, interest accrues on any unpaid tax from the original due date until payment is made.
It is essential to ensure that all worksheet calculations are accurately conducted and that the final amount due with the extension request is correctly calculated. Should the total of prior year's overpayments and current year's estimated tax payments exceed the estimated liability, the taxpayer can enter 0 on Line 4 and submit the form without payment.
Popular PDF Forms
How Do I Get a Quitclaim Deed - Conveys property ownership rights from one person to another in Tennessee.
How to File for Divorce in Tennessee - Details the civil case cover sheet and divorce certificate forms, explaining their purpose and submission requirements.
Ebt Tennessee - Address your family's essential needs by taking advantage of the assistance options provided through the Tennessee Department of Human Services application.